Key Takeaways
- A 100-amp breaker box typically meets the demands of most small—to mid-sized residential properties, providing balanced safety and reliability.
- Proper wiring techniques and adhering to current electrical codes are vital for safe and efficient installations.
- Periodic inspections and timely upgrades can prevent electrical hazards and keep your system operating at its best.
- Attempting electrical work without proper skills and permits increases the risk of fire and costly mistakes; professional help is highly recommended.
- Keeping informed about local codes and trusted safety resources is key to protecting your home and loved ones.
Table of Contents
- Why Choose a 100-Amp Breaker Box?
- How Breaker Boxes Work in Your Home
- Basic Steps for Wiring a 100-Amp Breaker Box
- Common Mistakes Homeowners Should Avoid
- When to Upgrade or Replace Your Breaker Box
- Essential Safety Tips for Homeowners
- Navigating Local Electrical Codes and Permits
- Stay Informed: Trusted Resources
Why Choose a 100-Amp Breaker Box?
Selecting a 100-amp breaker box is a practical and popular decision for homeowners who want to ensure reliable power distribution for their daily needs. This size panel is well-suited for most homes built in the last several decades, accommodating the power requirements of lighting, standard appliances, and moderate electronic use. With growing energy demands from modern conveniences, it’s essential to have a foundation that can handle peaks without struggling or causing frequent trips. Opting for a professional 100 amp breaker installation ensures your panel is code-compliant and tailored to your unique usage. Beyond just the initial installation, professionals can advise homeowners about future upgrades should energy usage change, ensuring ongoing safety and adaptability.
Along with ample capacity for daily routines, a 100-amp breaker box offers an optimal mix of affordability and scalability. Homeowners gain peace of mind knowing they have the power needed for their current situation and extra room for add-ons like a hot tub, media room, or energy-efficient appliances. Insights from major utilities like PG&E underscore the importance of matching your breaker size with your home’s energy draw to reduce risk and avoid unnecessary expenses.
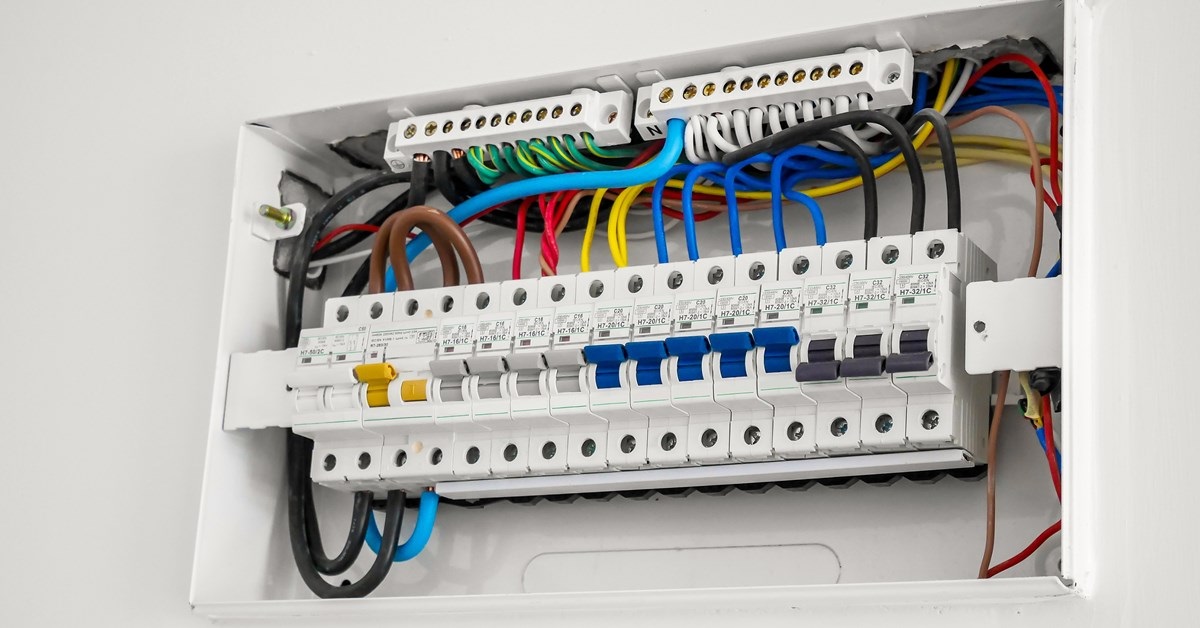
How Breaker Boxes Work in Your Home
The breaker box, or electrical panel, is the heart of your home’s electricity management system. Electricity from the grid arrives through service wires that feed into the panel, dividing the power among separate circuits. Each circuit is protected by its breaker, designed to cut off the flow of electricity when it detects an overload or a short circuit—a simple, effective way to prevent overheating and electrical fires. Breakers come in different amperages, and each should match the maximum load expected on its corresponding circuit. Understanding which breaker controls which part of your home is not just practical for troubleshooting—it’s a crucial step in routine maintenance and emergency scenarios. Clearly labeled circuits help households react quickly when a breaker trips, minimizing inconvenience and potential danger from exposed wiring or untamed power surges.
Electrical panels are typically installed in basements, garages, or utility closets, providing easy access to all circuit breakers. Homeowners should review their panel labeling after significant home changes to keep the information current, preventing confusion when swift action is needed. Thoughtful organization inside the panel also reduces the risk of accidental mistakes and makes future service visits much more productive.
Basic Steps for Wiring a 100-Amp Breaker Box
Wiring a 100-amp breaker box is a delicate process with several clearly defined steps to ensure safety, accuracy, and longevity. While only a brief overview is presented here—and the actual work is best left to licensed professionals—the process begins with turning off the main power. Installing the panel securely, usually against a stud or fire-rated backing, creates a safe and stable housing for all components. The main service wires are routed through the conduit into the box, where careful insulation stripping and secure fastening to the main lugs are critical to preventing future hazards like loose connections or electrical arcing, both common causes of dangerous malfunctions. Next, individual branch circuits are organized and attached to breakers according to their intended loads, whether lights, outlets, or heavy-duty appliances. All ground wires must be firmly attached to the ground bus, and neutral wires must be connected to the neutral bar, following strict codes for separation and accessibility.
The work finishes thoroughly inspecting each connection, double-checking for tightness, proper labeling, and code compliance before restoring power. According to the National Fire Protection Association, electrical systems that are professionally installed and regularly maintained dramatically reduce the chance of house fires and outages, underscoring the value of informed careful installation.
Common Mistakes Homeowners Should Avoid
Even small mistakes in breaker box wiring can have severe consequences. Many homeowners, hoping to save money, try tackling their electrical panels without enough knowledge of the required wire gauge, breaker capacity, or proper grounding techniques. Overloading the panel—by adding too many circuits or pairing heavy appliances on the same breaker—is a frequent error that can result in overheating and eventual fire risk. Using wires not rated for the required amperage can also create similar hazards, as undersized wires struggle to carry electrical loads safely. Some homeowners neglect to bond their ground and neutral buses per code, which introduces the possibility of shock or code violations that can complicate home sales.
Ignoring repeated breaker trips, flickering lights, or buzzing sounds from the panel is tempting, but these are all urgent warnings. Sometimes, these symptoms are traced back to poor connections or aging hardware that can easily be corrected by a skilled electrician if addressed early. Lastly, failing to stay up-to-date with local code changes leaves homeowners vulnerable to fines, insurance complications, and real safety threats.
When to Upgrade or Replace Your Breaker Box
For many families, a home’s electrical needs naturally increase over time. Whether it’s remodeling a kitchen, purchasing high-demand appliances, or bringing home an electric vehicle, your reliance on power grows. A 100 amp panel may have been perfect when you moved in, but significant life changes signal it’s time to reassess your system’s capacity. Upgrading your breaker box can boost resale value and provide safer, more consistent energy delivery for years. It’s recommended by the National Fire Protection Association that you have your panel inspected at least once every 20 to 30 years, as advances in wiring standards and safety mechanisms have made newer systems far more robust and reliable.
Rust, frequent tripping, or visible corrosion on breakers are immediate signs that replacement is likely overdue. Similarly, call an electrician immediately if your panel feels warm to the touch or produces an odor. Dated or obsolete panels often lack proper arc or ground fault protection—modern safety essentials that offer peace of mind for every household.
Essential Safety Tips for Homeowners
When working around or inside a breaker box, caution should always come first. Before opening the panel, shut off the main supply using the exterior disconnect if one is present. Always wear shoes with good rubber soles and use tools that have insulated handles to avoid risky shocks. Keep the area around the breaker box clear of clutter, flammable materials, and water sources, lowering the risk of fire and accidental short circuits. If your home is over three decades old or you have completed several renovations, a full-panel inspection by a certified electrician is wise. This small step can prevent problems like degraded insulation, loose wire connections, or undetected water damage.
Label every circuit clearly and keep an updated chart near the panel. Not only does this simplify future repairs, but it could also help you—or a safety professional—act quickly to isolate an issue in an emergency. Unusual sounds, burning smells, or warm breakers should never be ignored. These signs almost always require immediate, professional attention.
Navigating Local Electrical Codes and Permits
Strict regulations govern breaker box installation and replacement to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards. These rules cover everything from the type of wiring used to the placement and labeling of circuits. In most municipalities, homeowners must obtain permits before starting any major electrical project. This process often involves submitting a project outline and scheduling inspections at key points—typically before closing the walls and upon completion. These steps confirm the work aligns with the most current version of the National Electrical Code (NEC), though local jurisdictions may adopt unique amendments or stricter requirements. Ignoring permitting rules or attempting shortcuts risks fines and failed inspections and can lead to dangerous electrical issues that remain hidden until it’s too late. Even skilled DIYers should stay up-to-date with code changes as electrical standards evolve regularly. When uncertain, contacting your city’s permitting office or consulting a licensed electrician can clarify local expectations and ensure peace of mind.
Stay Informed: Trusted Resources
Electrical safety is never a one-time effort. By referencing recognized guides like the Electrical Safety Foundation International’s home electrical safety checklist, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of routine maintenance and warning signs. Continual learning can help you identify issues before they escalate, make informed decisions about upgrades, and ensure you’re working within all safety and legal parameters. Connecting with skilled local electricians is equally valuable, as codes and recommended best practices frequently evolve.
Keeping your 100-amp breaker box in good working order is more than convenience—it’s a commitment to the safety, efficiency, and comfort of everyone who shares your home. With regular care and an informed approach, you can rest easy knowing your electrical system is built to handle the power needs of today and tomorrow.